10 Principles of Trustcasting in the Web Marketing Universe
February 2010
By The Author

In today’s marketplace, the Web is where customers are won and businesses grow.
It starts with a
great website – one that has successfully confronted and conquered the challenges of providing a beautiful interface, engaging content and utility beyond your primary offering. However, even the best site is only the first step; it’s the foundation upon which you can start to develop a community around your brand.
Once you’ve launched your site, you’ve effectively set up shop and opened the doors. That’s when the real work begins.
To get and keep customers, you must master the
Web marketing universe beyond your own site. You must actively seek out those whose needs, desires and interests align with the products or services you offer, draw them in and engage them in conversation.
This is where
trustcasting, the ongoing process of building and maintaining trust between a business and its customers, comes into play.
As you venture out into the Web marketing universe, you’ll find a myriad of different channels for reaching and interacting with potential customers – from Facebook and Twitter to blogging, videocasting and more. While it may initially feel like daunting and unfamiliar territory, the key to navigating this new landscape successfully is to ensure that all of your efforts are driven by the motivation of establishing and keeping trust.
As long as you always follow the principles of trustcasting, you will inevitably turn contacts into customers, customers into fans and fans into evangelists, all while cultivating a vibrant virtual community.
Following are some smart trustcasting strategies that you can use to gain trust and grow your business in the Web marketing universe.
1. Give a little, gain a lot.
The first step in gaining the trust of a potential customer who may not yet be familiar with or invested in your brand is to offer them something of value in order to establish that you are interested in forming a relationship that is mutually beneficial, rather than simply self-serving.
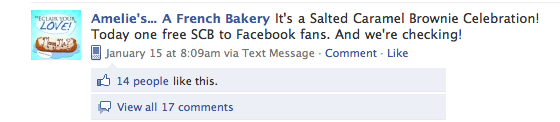
An easy way to open the lines of communication is to reward the act of becoming your friend, fan or follower on a social networking site with a special discount or promotion. Amelie’s...A French Bakery in Charlotte, N.C., recently rewarded their Facebook fans with a free favorite treat, driving their number of fans from 2,500 to over 3,000 in just over two weeks’ time.
2. Once you’ve captured their attention, don’t betray their trust.
Just because someone has added you as their friend or fan on Facebook or chosen to follow you on Twitter doesn’t give you free reign to bombard them with self-promotional messages and sales pitches.
In order to keep their trust and earn their loyalty, you must continue to engage them with offers and information they can’t get elsewhere. Develop a reputation in the Web marketing universe for consistently delivering quality content that is helpful to your customers or advice that makes their lives easier or better, even if in a small way.
For example, a specialty foods shop could maintain a blog featuring useful tips for entertaining. From easy recipes to food and wine pairings to simple centerpieces to fun themes, this information would resonate with the type of person who would be inclined to frequent such a shop. By providing fresh content on a regular basis (promoted through Facebook and Twitter), the shop owner keeps the reader engaged, building trust with every post and reaping the benefits when it’s time for their next dinner party.
Granted, this requires an ongoing commitment of time and energy, but the reward is turning a friend into a customer into an evangelist for your brand.
3. Throw away your “i” key.
Okay – maybe not literally. But do use it sparingly.
According to a study of 60,000 tweeters by viral marketing scientist
Dan Zarrella, those who use social language (“we,” “you’) or language that describes relationships and communication are more successful in attracting followers than those who tend to talk more about themselves (“I”).
Why, you ask? Then ask yourself this, what if you found yourself in face-to-face conversation with someone who talked exclusively about themselves? Would you want to continue interacting with that person? Would you have any reason to believe that person had any concern for you, your desires, your needs or your priorities? Certainly not.
Even if the culture of the Web marketing universe is unfamiliar to you, the rules of engagement are no different. Don’t lose sight of the fact that, at the end of the day, you are one real person relating to another real person. Behave online as you would standing in a room with your followers.
Invest in the lives of your customers, show genuine concern for the things that matter to them, demonstrate willingness to help in ways that do not immediately benefit you, and you will make great strides in building trust.
4. Power to the people.
Nothing you could ever say about your own company will hold the same level of credibility as the word-of-mouth reviews of your customers.
The good news about this is that in the era of social media, it has become second nature for people to post online about almost everything they experience in real life. Use this tendency to your advantage by giving your customers a soap box to tell others about you and build trust on your behalf. For example, creating a Facebook group provides a centralized place where customers can post reviews and comments.
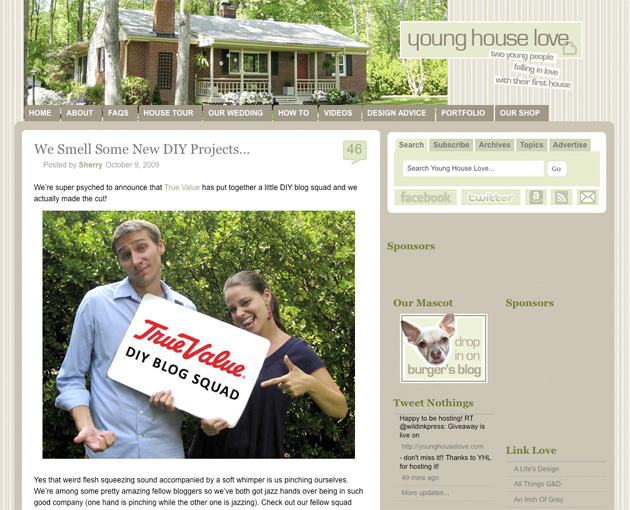
Taking this idea one step further, find those who already have a loyal following, and empower them to evangelize for your brand. In 2009, True Value launched a three-month “DIY Blog Squad” promotion. They identified five highly popular home improvement blogs and challenged the bloggers to take on a project using materials from their stores. Although the bloggers were compensated by True Value for these materials and their time to write about their experiences, they were free to share their own opinions and were not paid to publish positive comments.
Through this promotion, True Value reached legions of loyal readers and eager DIY-ers across the country, taking advantage of the trust in the credibility of the bloggers’ reviews to earn trust for their brand by extension.
5. Don’t underestimate the “good” of the greater good.
Today’s consumers want to know that the companies they do business with are committed not only to making their own lives easier but also to making a contribution to the community as a whole.
Being a good corporate citizen demonstrates to the public that there are principles behind your brand. In doing so, you forge bonds of trust with your customers, who perceive your actions as evidence that you share their values and, by extension, that your motives are rooted in more than simply what’s best for your bottom line.
The Web marketing universe offers great opportunity to practice social responsibility in ways that also engage your fans or followers. For example, Yoga Today, an virtual yoga studio that offers video classes online, is currently donating a portion of their profits to the American Red Cross for their Haiti relief efforts.

Although it requires a small investment on the part of Yoga Today, this promotion will pay dividends in spades. Not only will it help drive traffic to their primary site and give customers added incentive to sign up for classes in February, it also gives all followers – whether or not they choose to act on the offer – reason to trust in the company’s values.
6. Respond in real time.
In the digital age, you can’t afford to sit back and wait for someone to come across your ad in the phone book. Don’t just hope that they’ll remember your ad when the need for your product or services arises.
Instead, be proactive in the Web marketing universe. Use tools such as TweetDeck or monitter to track mentions of keywords and locations of tweeters. Identify people who have problems or issues that you can address, and reach out to them with helpful advice and solutions. By taking the time to meet their needs through a one-on-one approach, you can easily gain the trust and loyalty of a new customer or even turn an angry customer into a fan for life.
7. Be generous with your expertise.
You know your stuff better than anyone. Share that expertise with the world, and you’ll not only gain the trust of your prospective customers but also establish yourself as a credible source of useful information.
This rule goes against conventional wisdom about growing a business. Companies tend to shy away from sharing their knowledge, fearing that if they reveal too much, prospects will no longer need to do business with them.
The truth is that you don’t need to give away trade secrets to build trust. An HVAC repair business doesn’t need to post detailed manuals on maintaining every model they service, nor does a dentist need to refrain from writing about home whitening products for fear that prospects won’t come to the office. However, tips on performing a seasonal check on an air conditioning unit to spot problems and save money – along with tips on how to take proper care of your teeth at home – are good examples of how these types of businesses can effectively share their expertise with the greater community and create a reputation as a trusted resource while simultaneously growing their customer base.
8. A little humility goes a long way.
Be gracious and genuine. Admit mistakes. Personally address and correct the issue. Apologize. Customers are not only king; they are picky, they are fickle and they are demanding. Many businesses preach that the customer is always right, but few practice it.
One delighted customer can spread your message and be an evangelist for your brand. The opposite – the dissatisfied customer – can cause 10 times the devastation.
Addressing issues that arise in the Web marketing universe must be approached differently than dealing with problems face-to-face at the checkout counter. Generally speaking, when you respond to a complaint online, such as on a Facebook group page, you are doing so in a public forum.
As such, it is critical always to err on the side of humility. Don’t go on the defensive. Instead, take the criticism to heart, thank the customer for their feedback and examine the matter closely.
Be gracious and genuine. Admit mistakes. Personally address and correct the issue. Apologize.
Don’t fear that you will lose trust by acknowledging fault or error. Instead, your followers, fans, other customers, prospective customers and the community at-large will recognize your humility and sincerity in fixing the problem, and the resolution will blossom into greater trust.
9. Turn ideas into action.
The Web marketing universe offers companies the ability to be constantly tuned in to their customers’ needs, wants and opinions in ways never before possible.
To make the most of this opportunity, you must be vigilant in keeping tabs on your wall posts on Facebook, monitoring mentions of your company on Twitter and following your reviews on Yelp or any number of other sites driven by user contributions.
As feedback comes in, it is important to respond promptly and keep the conversation going in order to keep your fans and followers engaged. Even more important, however, is to carefully examine the information you are receiving. Take note of patterns and trends. Are there certain requests or concerns that arise repeatedly?
Taking this one step further, you can use your Facebook page and Twitter account to solicit input from your customers. For example, a coffee shop could take an informal survey of their Facebook fans to get feedback on their hours of operation or whether or not live music would be a welcome addition.
You don’t need to respond to the wishes and whims of every customer. However, if you can identify a legitimate void or an area where improvement can be made based on the comments you are reading, you should take action.
While the trust-building effects of these kinds of changes are not as immediate as interacting with fans on Facebook or followers on Twitter, they are nevertheless real. Over time your customers will recognize and appreciate that you take their input to heart and tailor your products or services to better meet their needs.
10. Community-building is serious business, but that’s not to say it can’t also be fun.
Remember when you had your first delighted customer? Or accomplished that first big project? Or you first heard your company name being announced?
The fun of business – and this is not just for small business – is in applying passion. And if you truly love what you do, customers will recognize and respond to your passion, and they will invest their trust in you.
The very nature of trustcasting is that people want to interact with people, not companies. Be real. Be yourself.
Take an example from two competing heating and air conditioning repair companies in Charlotte, N.C. – Brothers Heating and Air and Morris-Jenkins.
Both offer tips and helpful information. Both are out to create a reputation. Both have extended themselves to the greater community beyond their own websites. Both use their actual employees and customers in their commercials.
The fun of business – and this is not just for small business – is in applying passion. Brothers has your standard advertising. The announcement of their service, their specials, pictures and videos with reminders that they are everywhere.
Morris-Jenkins adds something more to the equation. Their ads and photos show the smiling faces of everyone in the company. They paint a picture that says they simply love what they do.
That sense of passion comes out in the greatest measure through their television commercials that show their employees smiling and singing their seasonal catch phrases (“You’ll have cool air at your house tonight” or “You’ll have warm heat at your house tonight!”).
In fact, the ads have been running for so long now, they have become a bit of tradition in the Queen City.
Both companies strive to do their own form of trustcasting, but Morris-Jenkins clearly has fun doing theirs. It not only translates to better business inside, but better growth as people connect the name and the jingle with friendly service, honesty and a promise of service delivered quickly when it’s needed.
Start Today
The practice of trustcasting in the Web marketing universe is a rhythmic business process that you must adopt to replace the carpet-bombing tactics of old marketing if you want to get ahead of the competition in today’s marketplace.
Given the level of time and focused attention required, this may seem like a tall order, especially for a small business. However, this is where a qualified trustcasting agency can help. They can not only guide you through the Web marketing universe but can also work with you to execute these trustcasting principles, assuring your long-term success in getting customers and growing your business.
Great authors are defined by their ability to set fire to the written word. All too often in today's digital information age, that creative spark is stifled, leaving the Web littered with content that is lifeless and ineffectual. Fame Foundry's Author has made it his mission to revive the act of writing as an art form, harnessing the power of language to command attention and ignite a following. It's the difference between telling a story and building a legend.