Don't Call It a Comeback: Why Email Marketing Still Matters
August 2013
By Jason Ferster
"The reports of my death have been greatly exaggerated." – Mark Twain
There's been some chatter around the Web in recent years about the looming death of email at the hands of social media.
Scandalous as it sounds, though, many of us wouldn't mind seeing our bulging inboxes go away. The Telegraph recently highlighted a study connecting email to stress at work. Not surprisingly, participant stress levels spiked at points in the day when inboxes were fullest. Shocking revelation, right?
But whether the thought of email extinction unsettles or elates you, a closer look at its role in our work and lives reveals that the reports of email's death are greatly exaggerated.
State of the union email address
Social media may be doing the heavy lifting when it comes to sharing our lives, but email remains a valued, private and protected channel for conducting life and business online.
We use email to keep up with the brands, organizations and communities we care about through e-newsletters, news alerts, daily deals, group activity digests, etc.
We use it to conduct business online, such as registration for services, support requests, banking e-statements and payment confirmations. You can even get receipts emailed to you from the registers of many brick-and-mortar retailers now.
Ironically, even social media is using email to keep us engaged. How often do you receive notifications from Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and the lot about new followers, daily/weekly activity digests, new comments on conversations and suggestions for new connections?
Marketer's know the inbox is alive and well, and they're still pumping out white papers and webinars about email marketing. Email service providers like Constant Contact and MailChimp—and a half-dozen others—are still thriving.
Email still matters because it is so closely connected to our identities and our lives. It's less transient than social media. People delete their accounts—ask Facebook after a privacy policy change. Social sites rise and fall in popularity—last year it was Pinterest, this year Instagram. Some professionals hardly check their LinkedIn accounts. But nearly everyone online has an email account that they check regularly and some of us have had a particular address for 10, 15, and nearly 20 years.
So if email is closely connected to who we are as people, it's important that we as business growers frame email marketing efforts in this light. Forget open rates, click throughs, bounce rates, etc. for just a moment and let's focus on three keys to connecting with customers in their inboxes.
Key #1: Relationship
By signing up to receive your emails, customers are inviting you into their inbox—a personal space. They "opt-in" in faith that you will deliver value and not abuse the privilege.
This transaction of trust is as important as the ones involving money. Your email recipients are in fact customers even if they've never spent a penny on your products or services. They are paying for your email content with their time and attention.
Unfortunately, many businesses today don't understand (or ignore) this relationship dynamic and treat email like direct mail, using "spray and pray" tactics—"I've got a message to get out and a database full of email addresses. Let's do this!"
If you "e-blast" your customers, by the way, you may be guilty of this kind of marketing terrorism.
As customers welcome you into their inboxes, treat them with respect. Give them value. Be a guest they'll want to come back again and again. Essentially, don't be self-centered or rude.
Ultimately, the key to building relationships with your customers through email is the Golden Rule. Email as you would want to be emailed.
Key #2: Content
Email marketing is content marketing ... And the first key to great email content is to give subscribers what they want.
Give 'em what they want
If you offer multiple email subscription options for your customers—for example deals, company news, e-newsletters, etc.—then honor their wishes. If all I want is deals, don't send me your press releases.
If you don't segment your email content like this and basically have one big mailing list, then it's important to actively get feedback from subscribers to determine what types of content they're interested in—and how often want to get it, but more on that later. Consider polling your list once or twice a year to see which features they like best. Or better yet, make your emails "reply-able" and end them with a question like "How can we improve the content of our emails for you?" This type of engagement with the reader make the email more of a two-way conversation.
To increase trust and interest earlier, at the email sign-up form, make it clear what customers will be getting by subscribing. The more clarity you provide the more comfortable and more emotionally invested they will be.
Be interesting
It may sound obvious, but make it a priority to have something interesting to say or share with subscribers. Give them a reason to keep reading.
NextDraft is an an email newsletter published daily by Dave Pell in which Dave simply currates news from all over the web and delivers "The day's most fascinating news" right to your inbox. His description of NextDraft is better than any I could offer:
Each morning I visit about fifty news sites and from that swirling nightmare of information quicksand, I pluck the top ten most fascinating items of the day, which I deliver with a fast, pithy wit that will make your inbox vibrate with delight...
Imagine this: You'll actually look forward to email again. It's totally free and almost no one ever unsubscribes. The subscription form is up there, just a few pixels away. Go ahead. Give your inbox some awesome.
Just as captivating as the 10 intriguing stories Dave highlights each day is the smart writing he uses to set up each story and string them all together. Here's a sample:
Put a little art in their inbox
I always open emails from Berlin-based software firm 6Wunderkinder because they are the most beautifully designed ones in my inbox. Great design is core to the 6Wunderkinder brand and products, and this commitment carries over into their email, which always look great and announce something worth reading about. Here's a recent sample from my inbox:
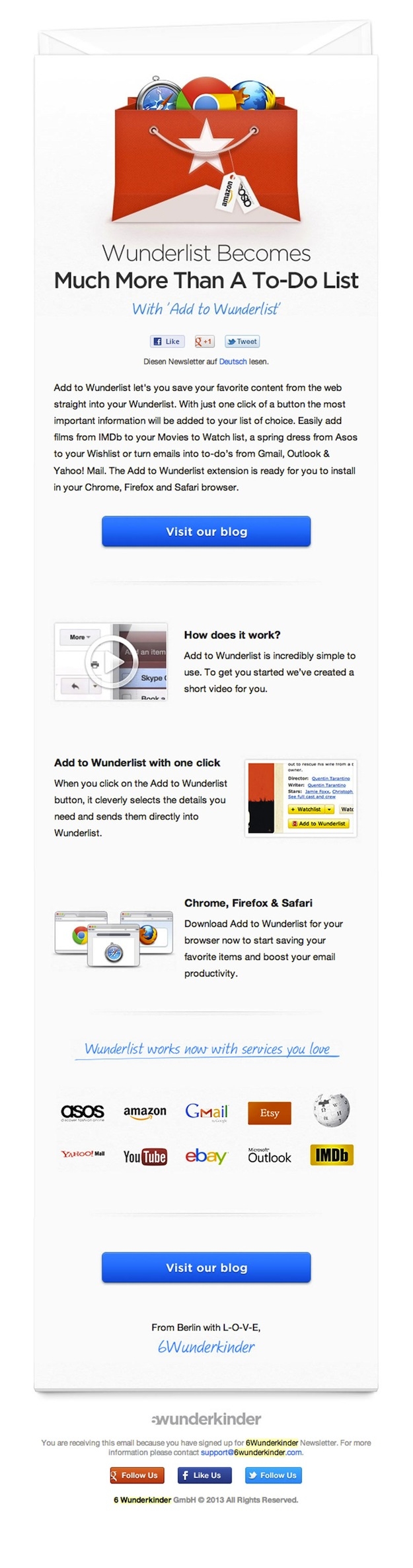
You don't have to be a design firm or developer to put together attractive html-based emails. Most email services providers have templates with drag-and-drop customization. But ... HTML-based email can be a little tricky in the ways it's rendered by various email software, so if in doubt, it's probably better to get some professional help.
Customize content to show you care
A growing trend in the email marketing world is email personalization, serving up different types of content to customers based demographics like location, sex or age as well as cues from their interactions with the brand or where they are in the sales pipeline. Personalization increases the value of your emails by providing content that fits more closely with customers interests and other characteristics.
For example, IKEA is a global brand, so the emails I get from their loyalty program, IKEA Family, are specific to my local store in Charlotte—not Stockholm. In the example below, they even offer a deal in collaboration with the local minor league baseball team, the Knights. And local store information—location, hours, and contact info—is included at the bottom.
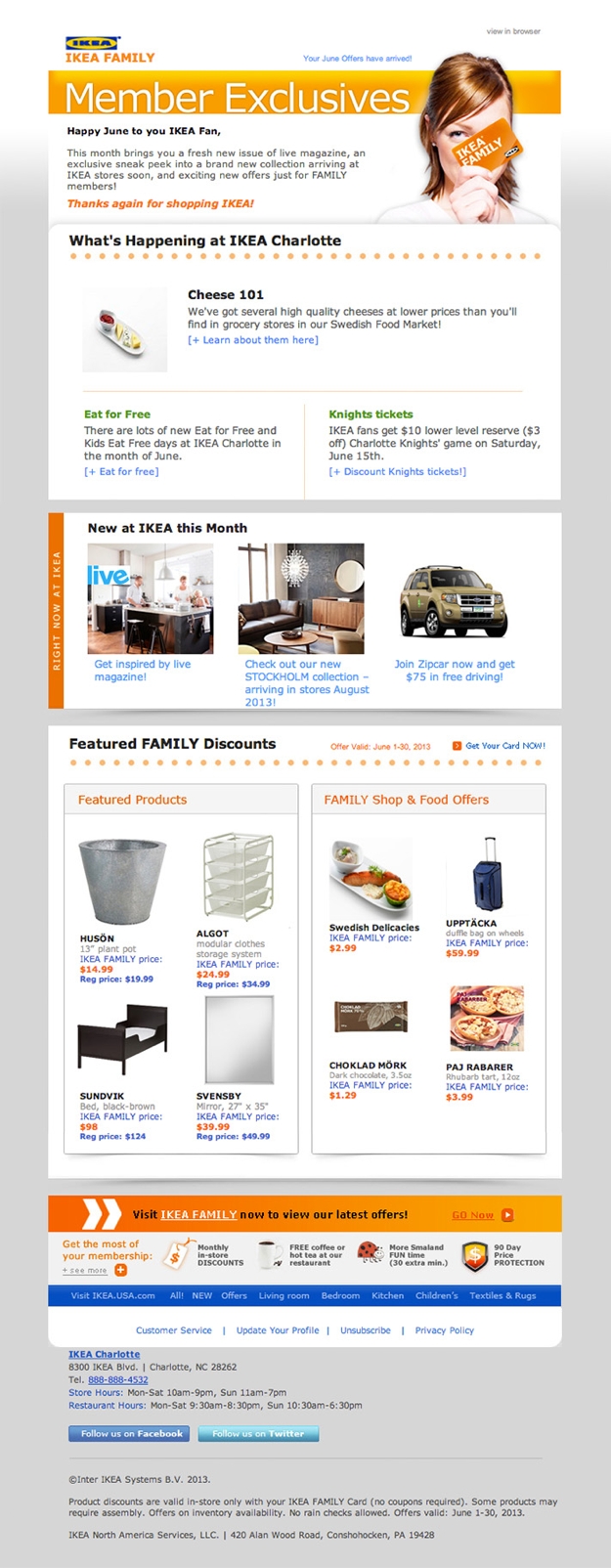
While this level of personalization involves some pretty robust marketing software, businesses without such resources can still tailor messages to specific groups of readers by segmenting their email lists through criteria like geographic location. Additionally, the major email service providers do offer some basic tools for email personalization. Just remember that the goal of any customization is to deliver a better, more personalized email experience to your customers.
Key #3: Frequency
A recent marketing study conducted by The Economist Intelligence Unit and Lyris, asked participants, "In your opinion, what frustrates you most about companies’ use of online communications?" Eighty percent of respondents chose "Too many unwanted email messages," outpacing the second place option by more than thirty points.
Most of us have grown accustomed to the tidal wave of information that is social media, so we're used to ignoring a lot of it. But email has to be managed. We generally touch each piece of mail, much in the same way as postal mail for centuries past. So the motivation here is to send only enough mail to provide value to subscribers, without being associated with inbox burnout.
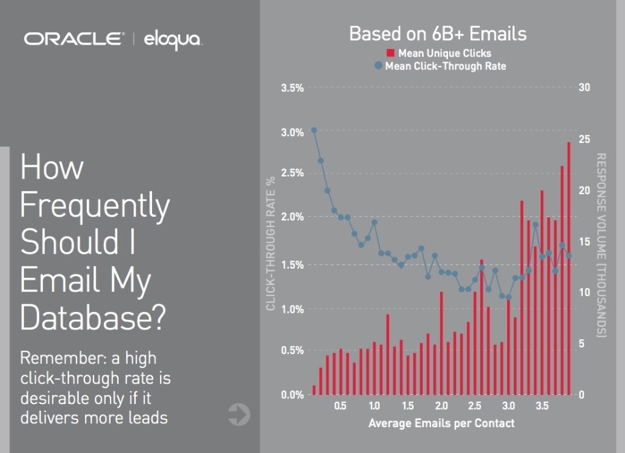
Research by Eloqua shows that a judicious frequency of emails sent isn't just good for the customer, it's good for campaign performance. In essence, it appears from the chart below that when it comes to getting customers to email marketing that gets results, less is more.
By day, Jason Ferster is the marketing manager of an IT consulting firm, where he contends daily with the marketing challenges common to small and mid-sized businesses. By nights and weekends, he writes about insights gained from those experiences. Visit FersterFiles.com for more or connect with Jason on Twitter.