An Oasis of Personality in the Desert of Website Design
July 2012
By Jeremy Girard
It’s a question every business – no matter the industry or niche – must answer: How do you differentiate yourself from the competition?
You can try to do it with your products or your prices, but anyone can come along with a similar product or service offering, and fighting a battle based solely on price almost always a losing proposition.
Differentiating yourself through the level of customer service you provide is a great idea, but the trick is that you have to draw someone in before you can win them over with your stellar service.
So then the question remains: how
do you stand apart from the crowd and draw positive attention to your business?
The reality is that all of the factors mentioned above – products, prices and client service – do play a role both in how you attract new customers and how you keep your existing customer base loyal.
Another differentiator that’s often overlooked, however, is your company’s personality – all of those intangible factors that are encompassed in your brand (think Apple vs. Microsoft) – and your website is the perfect platform to showcase that personality.
Nothing to fear
In the buttoned-up, suit-and-tie corporate world, the idea of showing personality can be a scary proposition, and many companies are afraid to try it for fear of alienating customers.
Present a personality that’s too casual and lighthearted, and you risk turning away clients looking for a more serious tone.
Present a very conservative, serious face, and you may come across as unfriendly and drive off those seeking a more personal approach.
This fear of alienating segments of your potential audience is why many companies seek the safety of the middle ground and institute a neutral, inoffensive design that they believe will appeal to everyone. What this really does, however, is cause both the company and their website to be perceived as unremarkable and unmemorable. By trying to appeal to everyone, they appeal to no one in particular.
As scary as it may seem, the risks of letting your company’s personality shine on your website are far outweighed by the benefits of creating a memorable experience for your customers.
Hey – I remember you!
When it comes to growing and promoting your business, blending in is never the right strategy. Make your website look and act just like everyone else’s, and you may not alienate anyone, but you won’t stick out in anyone’s mind, either.
Customers (and potential customers) who come to your site visit hundreds of other websites in any given week. The vast majority of them are driven by features and functionality to the point that if you took away the company logo, one would hardly be distinguishable from the next.
On the other hand, if your website offers something different and unexpected – whether in its imagery and visual design or in the tone and approach of the content – it will be like an oasis in the desert, a welcome change from the boring and bland.
When it’s time to make a purchase decision, who will they remember – the ones that did the same thing as everyone else or the one that marched to their own beat and had a unique voice?
Of course, your site and your company need to deliver the services and value that your audience is looking for, but making a powerful first impression upon your visitors and getting them to remember you is step one in winning their business. This approach can also help filter out clients that are right from those that may not be a good fit for your company to work with.
Finding the right fit
Even though your services may be applicable to a large and diverse audience, it’s important to ask yourself what your ideal customer looks like.
An ideal customer is one that not only has a need for your products or services but whose preferences for how those products or services are delivered mesh well with your organization. How can you expect to find that right fit if you’re not being “you”?
Let’s say your company is quirky and fun. If you do not embrace this personality in your marketing and on your website, you may appeal to a broader audience, but you will also attract potential clients who ultimately do not want to work with a company like yours.
In those cases, you will either lose their business when they realize you are not the type of organization they are seeking, or even worse, they will continue on with you but the relationship will be strained because your company is trying to be something they are not.
Instead of hoping to court everyone, try being yourself to attract customers that want to work with a company like yours. In the end, those engagements will be better suited, and often more profitable, for all parties involved.
Don't forget your internal audience
Maintaining a consistent personality between your website and how the company itself actually operates will also benefit your internal audience – that is, your employees.
By being true your company’s personality and being willing to show that personality to the world, you prove to your employees that you are committed to, and unashamed of, the culture you have created.
By doing this, your employees will feel more connected to the company and will enjoy a sense of pride in the organization that they’re part of. This allows them to be comfortable in speaking about the company without fear that they will saying something contrary to what the “marketing engine” is putting out there. By being true to your personality, you encourage every employee to become an advocate for your message in a way that is genuine and real.
Website designs with personality: A gallery
To show just how effective designing with personality can be, let’s take a look at a few examples of companies that have truly embraced these principles and wear their brand’s personality on their sleeves (or screens, as the case may be).
Northfield Savings Bank
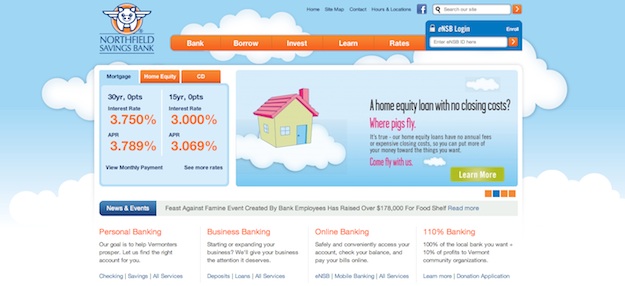
Banking websites are probably the last ones you’d associate with personality or fun, but the site for
Northfield Savings Bank uses both expertly on their site to set their institution apart.
From their playful “flying pig” logo to their story about those flying pigs, the website demonstrates unequivocally that this is no ordinary bank. For a customer who’s looking for a personal touch in their local bank – as opposed to a massive, faceless global institution – this site is surely a breath of fresh air.
Wishbone
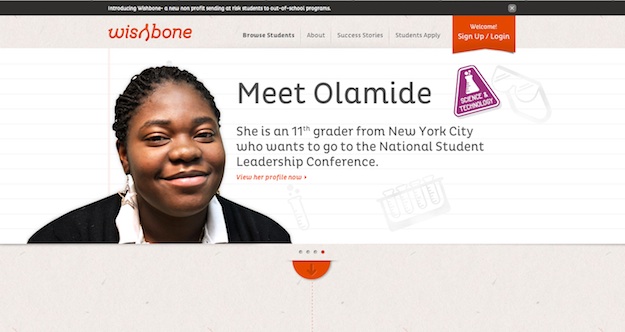
Non‐profit organizations are committed to their missions. This is good, but too often that dedication and seriousness translates into a boring, and therefore unmemorable, approach on their website.
Wishbone is an organization that sends “at-risk high school students to after school and summer programs.” The website certainly shows their passion for that mission, but it does so through the use of real photos of and personal stories from the students as well as fun animations that illustrate their process, which creates a very enjoyable, and ultimately very memorable, user experience.
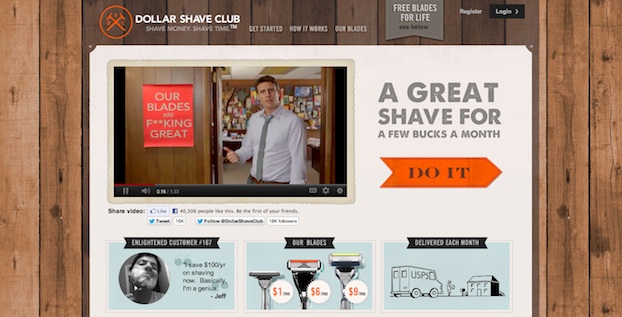
Dollar Shave Club

Normally, a “memorable” shaving experience is a bad thing, because it likely means something went horribly wrong.
But
DollarShaveClub.com offers a very memorable (and good) experience, welcoming new visitors with a wonderful and humorous video and carrying this playful approach throughout their entire site.
Rather than spending big bucks on endorsements from pro athletes or celebrities and presenting a high‐tech feel like their competitors do, Dollar Shave Club opts for a very real-world feel with textures of wood and torn paper. Compare those earthy textures and their comedic tone with
Gillette, for example, and you’ll see just how starkly different this approach is.
In this case, doing something different has not only created a memorable experience, but one that also promotes sharing. Dozens of friends and colleagues sent me the link to Dollar Shave Club’s website after it went viral.
So while this fun and kitschy approach may not be right for everyone who buys razors, it has captured the attention of many who not only appreciate its quirkiness but also happily share their love of the brand with others in their social circles.
Need more proof? Just compare the two companies’ videos on YouTube. As of this writing, Dollar Shave Club’s
"Our Blades Are F***ing Great" video is approaching 5 million views while Gillette’s
“Masters of Style” video, featuring celebrities Andre 3000, Adrien Brody and Gale Garcia Bernal, has yet to cross the quarter-million mark.
MailChimp
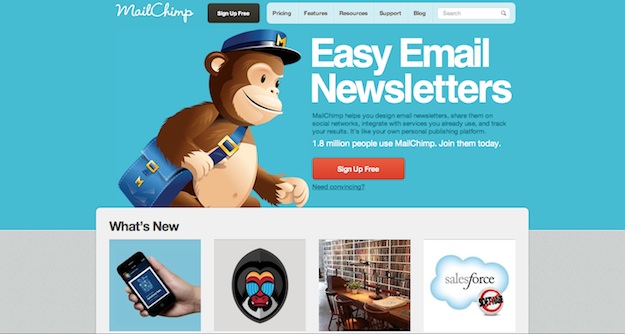 MailChimp
MailChimp’s lead user experience designer Aarron Walter has been touting the benefits of adding emotion and personality to websites for some time through his writing and speaking engagements, and that approach is very evident throughout the entire experience of MailChimp.com.
Compare their site, which is loaded with unique personality, to other email marketing providers such as
Constant Contact,
Emma or
VerticalResponse, and you will see the difference right away.
Those email marketing providers, and many others you will find, all employ a very similar approach on their website – one that quickly becomes unexciting and forgettable.
Go to the MailChimp website, however, and the giant illustration of company mascot Freddie von Chimpenheimer IV is one that’s sure to make a lasting impression. Delve still deeper into the site, and into their service, and you will discover just how unique MailChimp is – because anyone that can make email marketing enjoyable is definitely doing something right!
Run For Your Lives
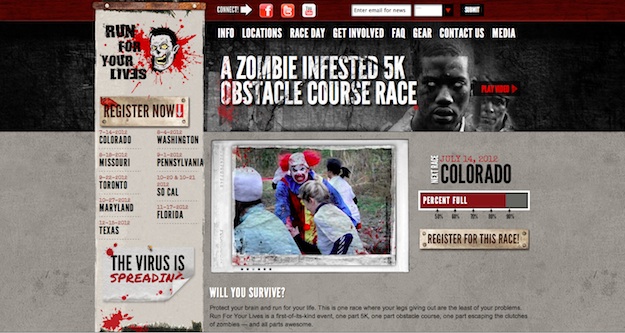
My father and my wife are both runners, so I’ve seen my share of websites for road races.
When I heard about the
Run For Your Lives Race, which is part running race and part obstacle course – all while hordes of mindless zombies chase after you to try to turn you into one of them – I knew I had to check out their website.
The race itself is certainly memorable, as anyone who has run it will surely tell you, and the organizers made sure that the same approach was used on the website. From dark textures and visuals used to complement the race’s zombie theme, to promotions like their contest to “win an all‐expense-paid funeral,” the site is perfectly on-brand, and like Dollar Shave Club, its unique approach promotes viral sharing.
No matter how many race websites you’ve visited before, I guarantee you’ve never seen one like this, and you won’t soon forget it!
GE
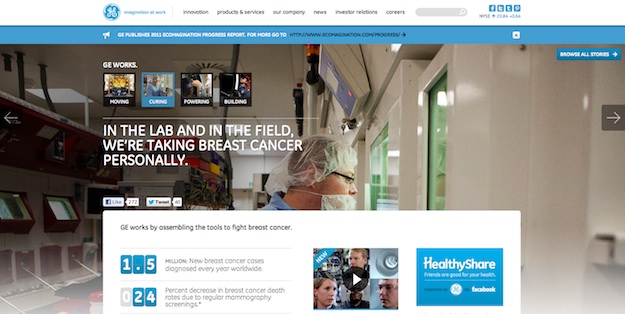
Humor and fun and zombies are not the only ways to make a lasting impression on website visitors.
GE has created an incredibly memorable experience on their site by focusing not only on the company’s technology and innovations but also on the people behind the brand and the impact they’re making in the real world.
Through powerful imagery, videos and personal stories, they have put a very human face on what could easily be a brand devoid of any type of emotional connection. In the process, they show that their company stands for much more than what they do or the products and services they offer.
Be memorable. Be yourself.
Be true to your company’s personality and embrace what makes you unique.
Stand boldly apart from the crowd and make a lasting impression knowing that your message may turn away some customers that aren’t really a good fit anyway, but it will also help you attract more of the ones that are right for you.
Or, to borrow the wise words of renowned business expert Dr. Seuss: “Be who you are and say what you feel because those who matter don’t mind and those who mind don’t matter.”
Jeremy Girard has been designing for the web since 1999. He is currently employed at the Providence, Rhode Island-based firm Envision Technology Advisors and also teaches website design and front-end development at the University of Rhode Island. In addition, Jeremy contributes regularly to a number of websites and magazines focused on business and the Web, including his personal site at Pumpkin-King.com.